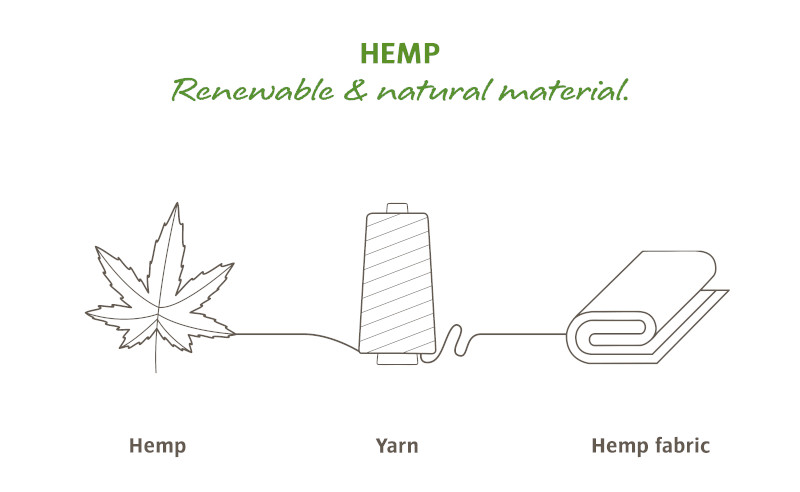
Hemp – first-class fabric with a sustainable impact
Hemp belongs to the mulberry family and is an annual plant that can grow up to 4 m high. It’s a rugged plant that requires little water, is naturally pest resistant and grows quickly.
Fiber hemp is primarily cultivated in China, but increasingly in Europe as well. Hemp needs less water than cotton for cultivation, and no fertilizers or pesticides. This makes it an environmentally friendly, renewable raw material.
In contrast to those plants grown for the production of narcotics, the hemp varieties grown for fiber use have a high fiber content rather than a high THC content. Therefore, these varieties are not suitable for the production of narcotics [SK7] .
The fiber is obtained from the stem of the plant, which consists of cellulose. After the hemp plant has been cut, the stems are left in the field to ripen and dry. The bast fibers are then removed from the stem in a labor-intensive mechanical process so that they can be spun into a yarn. This yarn is finally processed into hard-wearing fabrics that are made into high-quality and durable products.
The outstanding properties are persuasive
Hemp fibers have low stretch and elasticity and therefore tend to wrinkle. However, hemp fibers are very robust and the fabrics made from them have a high tensile strength. Due to their natural structure, hemp fabrics offer excellent breathability, good moisture management and do not absorb body odor.
Sometimes we also use recycled hemp, for example in our Lignum series where coarser materials are used. For this purpose, the waste that accumulates during the production of hemp clothing is, mechanically shredded, sorted according to color and spun into new yarn. This not only conserves raw resources, but also eliminates the step of dyeing the material.

| GRI: | 301-1 |